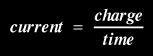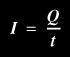Current Electricity Summary
Current electricity is a flow of charged particles.
In all dry conductors the flow is of electrons.
Electrons flow from negative to positive.
Conventional current flows from positive to negative
Current is represented by the symbol, I.
Current is measured in amperes (amps or A) with an ammeter.
One amp is equal to the flow of one coulomb* of charge per second. This translates to:
Or in unit terms:
Click here for examples of this formula in use.
The symbol for an ammeter:
RELATED TOPICS:
|